
The choice between LCM and NRV can significantly impact a company’s financial statements. LCM provides a conservative approach that prevents overstatement of inventory values, while NRV offers a more realistic reflection of the potential realizable value. Companies must carefully consider their industry, inventory characteristics, and applicable accounting standards when choosing the appropriate method. By examining real-world examples and case studies, businesses can better understand the practical applications and implications of each method, ultimately enhancing the reliability and accuracy net realizable value formula of their financial reporting. Inventory write-downs occur when the recorded cost of inventory exceeds its net realizable value. This adjustment is necessary to ensure that the inventory is stated at an appropriate value.
Detailed Breakdown of a Lower of Cost or Net Realizable Value Example
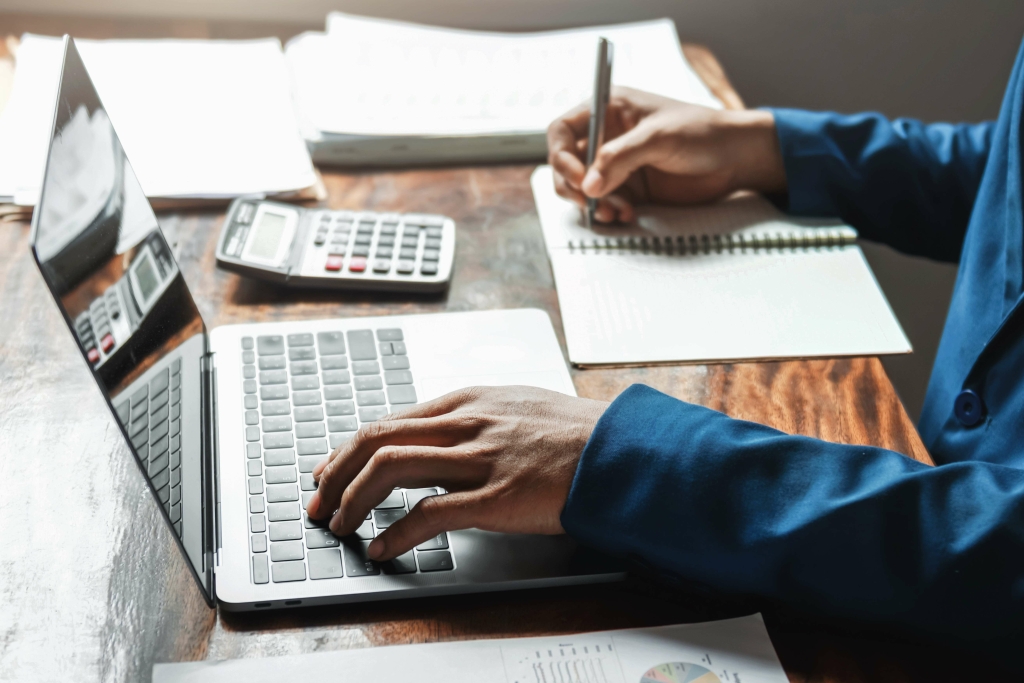
This granular approach results in the lowest possible overall inventory valuation and the highest immediate recognition of potential loss. Net Realizable Value (NRV) represents the estimated selling price of the inventory in the ordinary course of business. This estimated price must then be reduced by all what are retained earnings reasonably predictable costs of completion, disposal, and transportation.
Brief Example of a Write-Down Reversal (IFRS)
This conservative approach aligns with the accounting principle of prudence, which mandates that assets should not be overstated, and potential losses should be recognized promptly. The method chosen for inventory valuation can significantly impact a company’s financial statements. For instance, different valuation methods can lead to variations in reported net income, taxable income, and inventory carrying amounts. These variations can affect key financial ratios, such as the current ratio and Statement of Comprehensive Income inventory turnover ratio, which investors, creditors, and analysts use to evaluate a company’s performance and financial health. Accurate inventory valuation is crucial for financial reporting, as it affects asset values, profit reporting, and business decisions.
Financial Impact
- Specific identification assigns the actual cost to each individual item of inventory.
- The allowance to reduce inventory to LCM account is a contra asset account in the balance sheet, which is offset against the inventory account reducing its value to the lower of cost or market.
- If that number is lower than your cost, you have a potential write-down on your hands.
- Businesses can use NRV to determine the value of current assets, including their AR and inventory management.
- The term market referred to either replacement cost, net realizable value (commonly called “the ceiling”), or net realizable value (NRV) less an approximately normal profit margin (commonly called “the floor”).
- Both LCM and NRV play vital roles in inventory valuation, each offering unique advantages depending on the business context.
Choosing the appropriate inventory valuation method is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards. The method impacts not only the valuation of inventory on the balance sheet but also the cost of goods sold (COGS), gross profit, net income, and various financial ratios. Understanding the nature of inventory, market conditions, and regulatory requirements helps businesses make informed decisions, ensuring the reliability and relevance of their financial statements. These alternative valuation methods play a crucial role in accurately reflecting a company’s financial position. Inventory valuation rules help determine the worth of goods held for resale or production. Mechanisms for determining inventory values consider factors like FIFO (First In, First Out) and LIFO (Last In, First Out) methods.

- Accurate inventory valuation ensures that financial statements reflect a true and fair view of a company’s financial position, aiding stakeholders in making informed decisions.
- And if entity manages inventory as a whole then rule will be applied on totality basis on all types of inventory taken together.
- Since NRV is lower than the cost, the company should write down the value of the inventory to the lower amount, which is $90.
- These case studies highlight the importance of choosing the appropriate inventory valuation method based on industry practices, market conditions, and regulatory requirements.
- The Lower of Cost or Net Realizable Value (LCNRV) is an inventory valuation method mandated by accounting standards to ensure that inventory is not overstated on the balance sheet.
Next, the net realizable value is assessed by estimating the selling price of the inventory less any additional costs to complete the sale. By comparing the cost and net realizable value, the company can then adjust the inventory balance to the lower value, ensuring compliance with accounting standards and avoiding overstatement of assets. Determining the net realizable value involves estimating the selling price of inventory minus any expected selling expenses. This process ensures that companies accurately reflect the value of their inventory on the balance sheet, providing a more realistic representation of their financial position.
- However, it is impracticable to identify the lower of cost and NRVfor each individual item for a company where it has a large amounts ofinventory.
- The costs of disposal often include sales commissions, advertising expenses, and any necessary rework to ready the product for a customer.
- It is essential for accurately reflecting the cost of inventory on the balance sheet and determining the cost of goods sold (COGS) on the income statement.
- The expected selling price is the asset’s market value or the price at which the asset can be sold at any time.
- You can find information about companies’ treatment of net realizable value with respect to their assets on their annual reports.
Example – Accounting for LCNRV loss – directly in inventory

The two primary sets of standards that govern inventory valuation, including the application of LCM and NRV, are Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). The Weighted Average Cost method calculates the cost of inventory based on the average cost of all units available for sale during the period. This average cost is then used to determine both the cost of goods sold and the ending inventory. Accruing tax liabilities in accounting involves recognizing and recording taxes that a company owes but has not yet paid. Write-downs can be reversed up to the original cost if market conditions improve.• Under US GAAP (ASC 330), inventories are carried at the lower of cost or market. “Market” is not to exceed NRV nor be less than NRV minus a normal profit margin.